本文介绍了Java语言的企业开发特性,如JDBC,企业开发中常封装成各种工具、框架进行使用。
第 14 章 JDBC 和数据库连接池
14.1 JDBC 概述
14.1.1 JDBC 基本介绍
- 含义:Java DataBase Connectivity,Java 数据库连接,用于执行 SQL 语句的 JavaAPI,由类和接口组成,提供了个可以构建更高级工具和接口去访问数据库的基准。
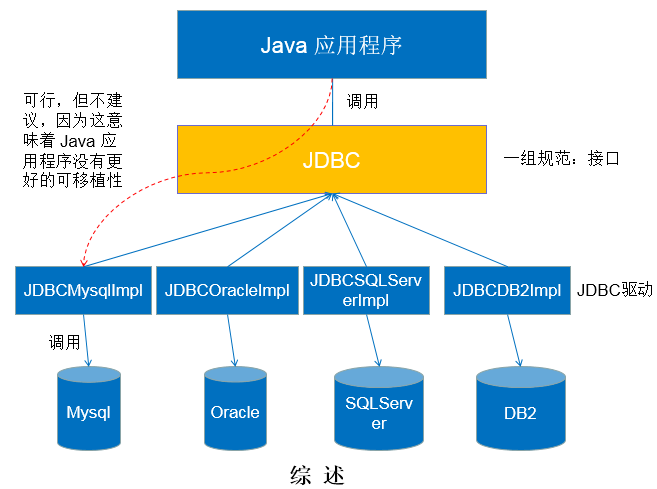
- 作用:java 程序员使用 JDBC,可以连接任何提供了 JDBC 驱动程序的数据库系统,从而完成对数据库的各种操作。JDBC 为访问不同的数据库提供了统一的接口,为使用者屏蔽了细节问题。
- 基本原理图:
- 模拟 JDBC 接口
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| public interface JdbcInterface {
public Object getConnection() ;
public void crud();
public void close();
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| public class MysqlJdbcImpl implements JdbcInterface{
@Override
public Object getConnection() {
System.out.println("得到 mysql 的连接");
return null;
}
@Override
public void crud() {
System.out.println("完成 mysql 增删改查");
}
@Override
public void close() {
System.out.println("关闭 mysql 的连接");
}
}
|
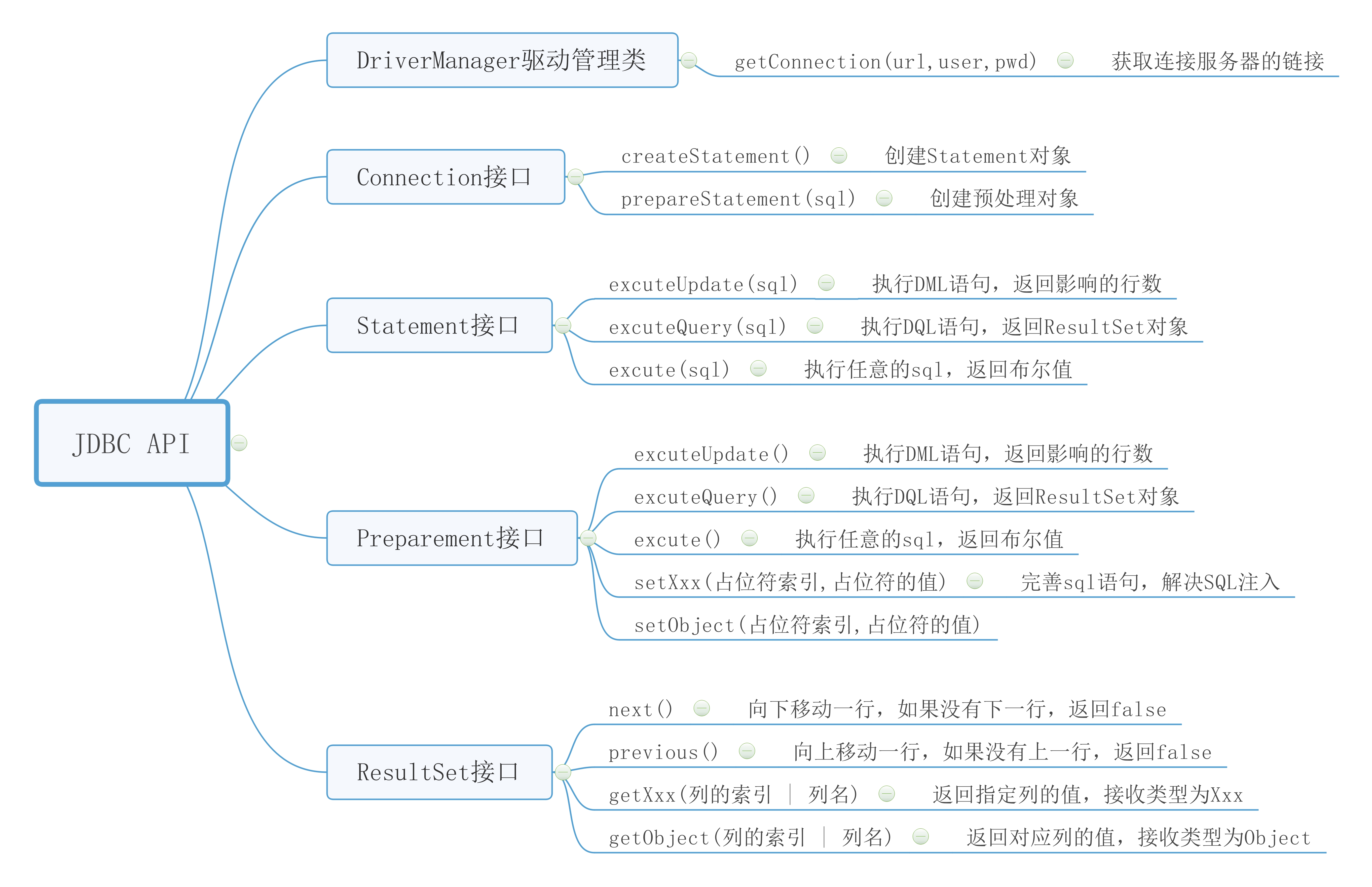
14.1.2 JDBC API
14.1.3 MySQLJDBC
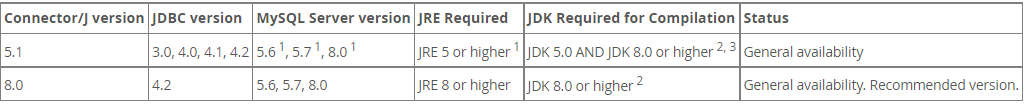
- 版本支持:
- 下载地址:
14.1.3 JDBC 程序编写步骤
- 前置工作:在项目文件目录中加载对应数据库的 JDBC 工具包
- 注册驱动——加载 Driver 类
- 获取连接——得到 Connection
- 执行 CRUD——发送 sql 语句(字符串)给 mysql 执行
- 释放资源——关闭相关连接
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
Driver driver = new com.mysql.jdbc.Driver();
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:13306/db01";
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty("user","root");
properties.setProperty("password","dimitre123");
Connection connect = driver.connect(url, properties);
String sql = "crud的SQL语句";
Statement statement = connect.createStatement();
int rows = statement.executeUpdate(sql);
statement.close();
connect.close();
|
- 解读:
- url:
jdbc:mysql:使用的连接协议localhost:连接地址(数据库地址)13306:数据库端口号db01:数据库名称- mysql连接的本质是socket连接
- properties对象:
setProperty()的user、password是规定好的
excuteUpdate(sql):dml语句时,返回的是影响的行数。
14.2 获取数据库连接(connection)的 5 种方式
14.2.1 使用 Driver 类的connect()方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
Driver driver = new com.mysql.jdbc.Driver();
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:13306/db01";
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty("user","root");
properties.setProperty("password","dimitre123");
Connection connect = driver.connect(url, properties);
|
- 存在问题:Driver()是第三方工具,依赖强、灵活性差,且属于静态加载。
14.2.2 使用反射获取 Driver,再使用connect()方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
Driver driver = (Driver)aClass.newInstance();
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:13306/db01";
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty("user","root");
properties.setProperty("password","dimitre123");
Connection connect = driver.connect(url, properties);
|
14.2.3 使用 DriverManager 注册驱动
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
Driver driver = (Driver)aClass.newInstance();
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:13306/db01";
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty("user","root");
properties.setProperty("password","dimitre123");
DriverManager.registerDriver(driver);
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, properties);
|
14.2.4 Class.forName 自动完成注册驱动,简化代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:13306/db01";
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty("user","root");
properties.setProperty("password","dimitre123");
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, properties);
|
- mysql 实现 java.sql 的 Driver 接口时,创建了静态代码块,自动执行
DriverManager.registerDriver(new Driver());
- 不写
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");也会正常运行,是因为 jdk1.5 之后使用了 jdbc4,会自动调用……\libs\mysql-connector-java-5.1.37-bin.jar!\META-INF\services\java.sql.Driver文件中的类名(com.mysql.jdbc.Driver)去注册
14.2.5 使用配置文件读取连接地址等信息
1
2
3
4
| user=root
password=dimitre123
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:13306/hsp_db02
driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream("src\\mysql.properties"));
String user = properties.getProperty("user");
String password = properties.getProperty("password");
String driver = properties.getProperty("driver");
String url = properties.getProperty("url");
Class.forName(driver);
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user,password);
|
14.3 结果集(ResultSet)
- 含义:执行查 DQL 语句返回的查询结果。
- ResultSet 对象保持一个光标指向其当前的数据行,最初光标位于第一行之前,next 方法将光标移动到下一行,并且由于再 ResultSet 对象中没有更多行时返回 false。可以使用 while 循环遍历。
- 使用:
ReultSet resultSet = statement.excuteQuery(sql);
- 方法:
- 底层:ResultSet 是个接口,底层的数据是表是一个 ArrayList
14.4 SQL 注入
- 含义:利用某些系统没有对用户输入的数据进行充分的检查,而在用户输入数据中注入非法的 SQL 语句段或命令,恶意攻击数据库。
- 访问数据库、执行 sql 语句的三种方法:
Statement对象【存在 sql 注入问题】PreparedStatement对象【预处理】CallableStatement对象【存储过程】
- 万能用户名:
1' or,万能密码:or '1'='1'
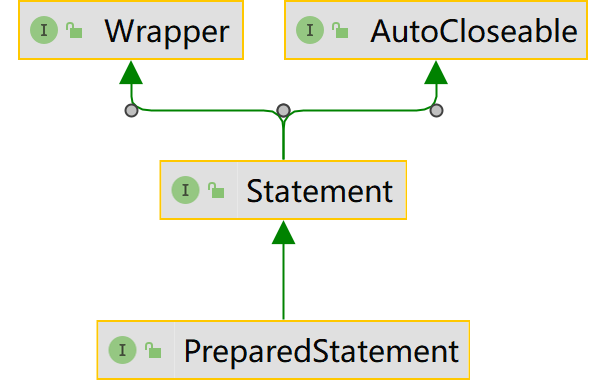
14.5 PreparedStatement 预处理的使用
- PreparedStatement 是 Statement 的子接口,可以使用 Statement 的方法(怎么使用的,Statement 的方法都是抽象的,是因为加载了 JDBCjar 包的原因吗?)
- 语法变化:
- 书写 sql 语句(定义 sql 字符串):使用
?代替参数值,作为占位符。
String sql = "select name , pwd from admin where name =? and pwd = ?";
- 创建 PreparedStatement 对象:
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
- 使用 PreparedStatement 的对象给 sql 语句的占位符赋值:使用
setXxx(int n, String str)
- n 表示
?在 sql 语句中从左至右出现的次序,从 1 开始。
- str 表示参数值。
- 调用
excuteUpade()或excuteQuery()方法,返回结果集。不需要再传入 sql 语句当作参数。
- 预处理好处:
- 不再使用
+拼接 sql 语句,减少了语法错误。
- 有效避免了 sql 注入问题
- 减少了编译次数,提高了效率
14.6 JDBC 事务
14.6.1 JDBC 事务介绍
- JDBC 创建一个 Connection 对象后,默认是自动提交事务,执行成功后不能回滚。
- 调用 Connetcion 对象的
setAutoCommit(false)可以取消自动提交事务。
- 调用 Connetcion 对象的
commit()可以提交事务。
- 调用 Connetcion 对象的
rollback()可以回滚事务。
14.6.2 应用场景
- 银行转账。
14.7 批处理(batch)
14.7.1 批处理介绍
- java 的批量更新机制允许多条语句一次性提交给数据库处理,提高处理效率。相当于公交车拉一车人。
- 批处理方法(statement 对象调用):
addBatch():添加需要批处理的 SQL 语句或参数excuteBatch():执行批处理语句clearBatch():清空批处理包的语句
- 使用:
- url 添加参数
?rewriteBatchedStatements=true
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| Connection connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
String sql = "insert into admin2 values(null, ?, ?)";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
for (int i = 0; i < 5000; i++) {
preparedStatement.setString(1, "jack" + i);
preparedStatement.setString(2, "666");
preparedStatement.addBatch();
if((i + 1) % 1000 == 0) {
preparedStatement.executeBatch();
preparedStatement.clearBatch();
}
}
preparedStatement.executeBatch();
JDBCUtils.close(null, preparedStatement, connection);
|
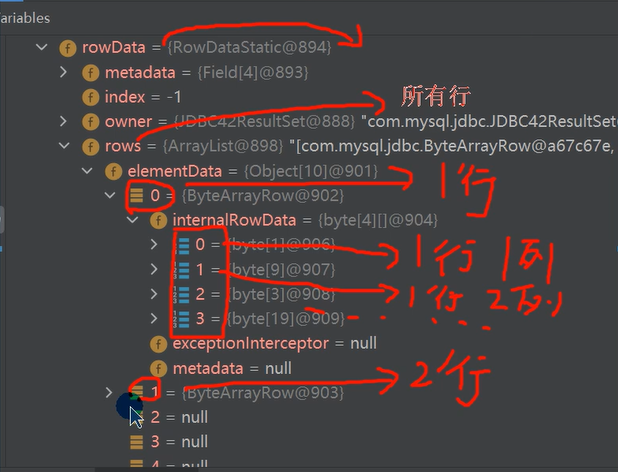
- 源码分析:
- 执行
addBatch()会创建 ArrayList - elementData => Object[]
- elementData => Object[] 就会存放我们预处理的 sql 语句
- 当 elementData 满后,就按照 1.5 扩容
- 当添加到指定的值后,就 executeBatch 批量处理会减少我们发送 sql 语句的网络开销,而且减少编译次数,因此效率提高
14.8 数据库连接池
14.8.1 传统方式连接数据库的问题
- 传统 JDBC 连接数据库使用 DriverManager 来获取,每次向数据库简历连接时,需要将 Connection 加载到内存中,再验证 ip 地址、用户名、密码(0.05~1s 时间),频繁进行数据库连接操作会占用系统资源,导致服务器崩溃。
- 每次连接数据库操作后,使用结束都应断开,如果程序出现异常而未关闭,将导致数据库内存泄漏,导致数据库重启
- 传统连接方式,不能控制创建的连接数量,如果连接过多,也可能导致内存泄漏,mysql 崩溃
- 使用数据库连接池(connection pool)技术,可以解决上述问题。
14.8.2 数据库连接池介绍
- 预先再缓冲池中放入一定数量的连接,当需要建立数据库连接时,只需从“缓冲池”取出连接,使用完毕后放回到“缓冲池”
- 数据库连接池负责分配、管理、释放数据库的连接,它允许用用程序重复使用一个现有的数据库连接,而不用重新建立。
- 当应用程序向连接池请求的连接数量超过最大连接数量时,这些请求会被加入到等待队列中。
- JDBC 的数据库连接池使用
javax.sql.DataSource表示,DataSource 是一个接口,该接口由第三方提供实现【提供.jar】
- 数据库连接池种类:
- C3P0:速度较慢,稳定性好
- DBCP:速度较快,但不稳定
- Proxool:有监控连接池状态的功能,稳定性不如 C3P0
- BoneCP:速度快
- Druid(德鲁伊):阿里提供,具有 DBCP、C3P0、Proxool 优点
14.8.3 C3P0 使用
- 将 c3p0 的 jar 包添加到开发环境,同 jdbc。
- 连接方式一:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
ComboPooledDataSource comboPooledDataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource();
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream("src\\mysql.properties"));
String user = properties.getProperty("user");
String password = properties.getProperty("password");
String url = properties.getProperty("url");
String driver = properties.getProperty("driver");
comboPooledDataSource.setDriverClass(driver);
comboPooledDataSource.setJdbcUrl(url);
comboPooledDataSource.setUser(user);
comboPooledDataSource.setPassword(password);
comboPooledDataSource.setInitialPoolSize(10);
comboPooledDataSource.setMaxPoolSize(50);
for (int i = 0; i < 5000; i++) {
Connection connection = comboPooledDataSource.getConnection();
connection.close();
}
|
- 连接方式二:使用 c3p0 的配置文件(整合了登录名、用户密码、连接地址、设置了连接数量等),放到 src 路径下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| <c3p0-config>
<named-config name="hello">
<property name="driverClass">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="jdbcUrl">jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/girls</property>
<property name="user">root</property>
<property name="password">root</property>
<property name="acquireIncrement">5</property>
<property name="initialPoolSize">10</property>
<property name="minPoolSize">5</property>
<property name="maxPoolSize">10</property>
<property name="maxStatements">5</property>
<property name="maxStatementsPerConnection">2</property>
</named-config>
</c3p0-config>
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
ComboPooledDataSource comboPooledDataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource("hello");
for (int i = 0; i < 500000; i++) {
Connection connection = comboPooledDataSource.getConnection();
connection.close();
}
|
14.8.4 Druid 使用

- 将 Druid 的 jar 包添加到开发环境,同 jdbc。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/girls?rewriteBatchedStatements=true
username=root
password=root
initialSize=10
minIdle=5
maxActive=20
maxWait=5000
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream("src\\druid.properties"));
DataSource dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
for (int i = 0; i < 500000; i++) {
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
connection.close();
}
|
14.9 Apache 之 DBUtils
14.9.1 基本介绍
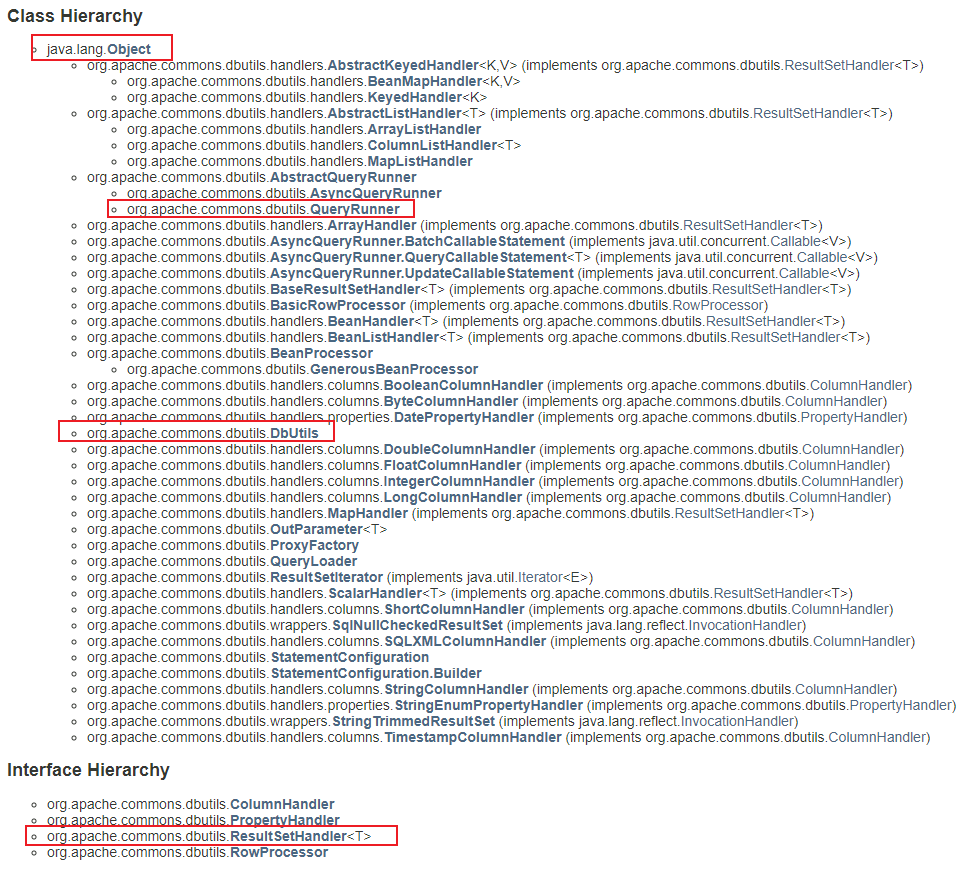
- commons-dbutils 是 Apache 组织提供的一个开源 JDBC 工具类库,它是对 JDBC 的封装。简化 Dao 层的操作。
- 树结构:
- 作用:将数据库查询得到的数据放到一个 ArrayList 中,即使连接关闭了,也能使用这些数据。(正常情况下连接关闭,就访问不到这些数据)。
- 使用步骤:
- 得到连接(使用数据库连接池等方式)
- 将 common-dbutils 加入库文件
- 创建 QueryRunner 的对象
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner()
- 执行 DQL,返回 ArrayList 结果集
- 返回多个对象(查询多行):queryRunner.query(connection, sql, new BeanListHandler<>(类名.class)
- 返回单个对象(查询单行):queryRunner.query(connection, sql, new BeanHandler<>(类名.class)
- 返回单行单列对象(对象类型为 Object):queryRunner.query(connection, sql, new ScalarHandler<>()
- 执行 DML,返回受影响的行数。
- queryRunner.update(connection, sql, ?的值)
- 底层分析:
- 调用 query()方法时,底层会创建 PreparedStatement、ResultSet、 一个接收结果的 Object 对象
- 底层调用 handle(查询结果),利用反射机制将查询到的结果传入到 Object 对象里
- 执行完毕关闭结果集、statement
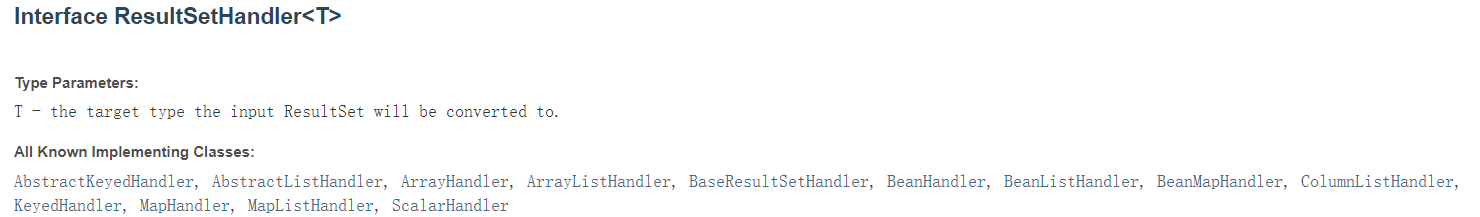
- ResultSetSHandler 接口实现类的主要作用:ResultSetSHandler 用于处理 java.sql.ResultSet,将数据按要求转换为另一种形式。
14.9.2 模仿 dbutils,理解原理
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
| public ArrayList<Actor> testSelectToArrayList() {
Connection connection = null;
String sql = "select * from actor where id >= ?";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet set = null;
ArrayList<Actor> list = new ArrayList<>();
try {
connection = JDBCUtilsByDruid.getConnection();
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setInt(1, 1);
set = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
while (set.next()) {
int id = set.getInt("id");
String name = set.getString("name");
String sex = set.getString("sex");
Date borndate = set.getDate("borndate");
String phone = set.getString("phone");
list.add(new Actor(id, name, sex, borndate, phone));
}
System.out.println("list 集合数据=" + list);
for(Actor actor : list) {
System.out.println("id=" + actor.getId() + "\t" + actor.getName());
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtilsByDruid.close(set, preparedStatement, connection);
}
return list;
}
|
14.10 Dao 和增删改查方法
14.10.1 Dao 层及 BasicDao:与数据库的相关操作
- Dao:data access object:数据访问对象
- Dao 中的方法均为”单精度方法“——一个方法只干一件事。
- Service 层中的方法可以是”非单精度方法“,一个方法可以干好几件事。
- 如 Dao 中的添加只是添加,Service 层中的添加还有先查询(判断是否重复)的功能,然后才是添加。
- 根据数据访问对象设计的类叫 Dao,高度抽象的该类叫 BasicDao。
- 在 BasicDao 的基础上,设计继承自其的实现特定与数据库操作的 Dao 类,可以更好完成开发任务。
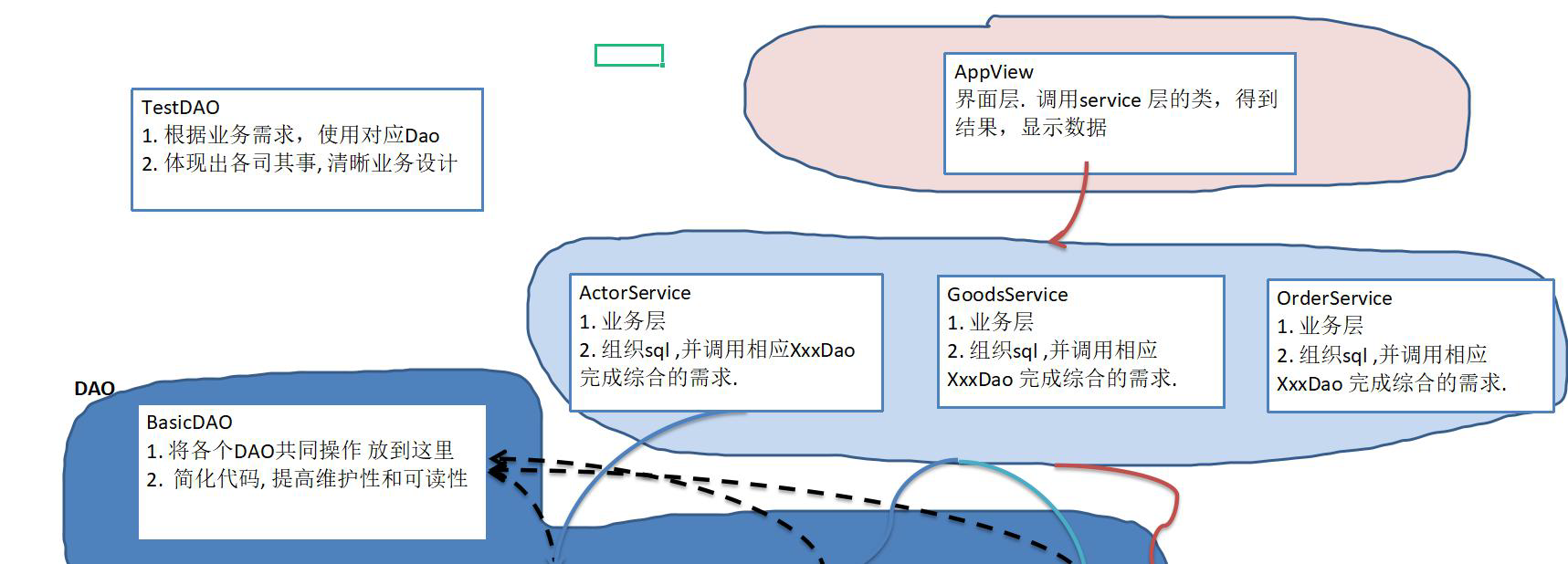
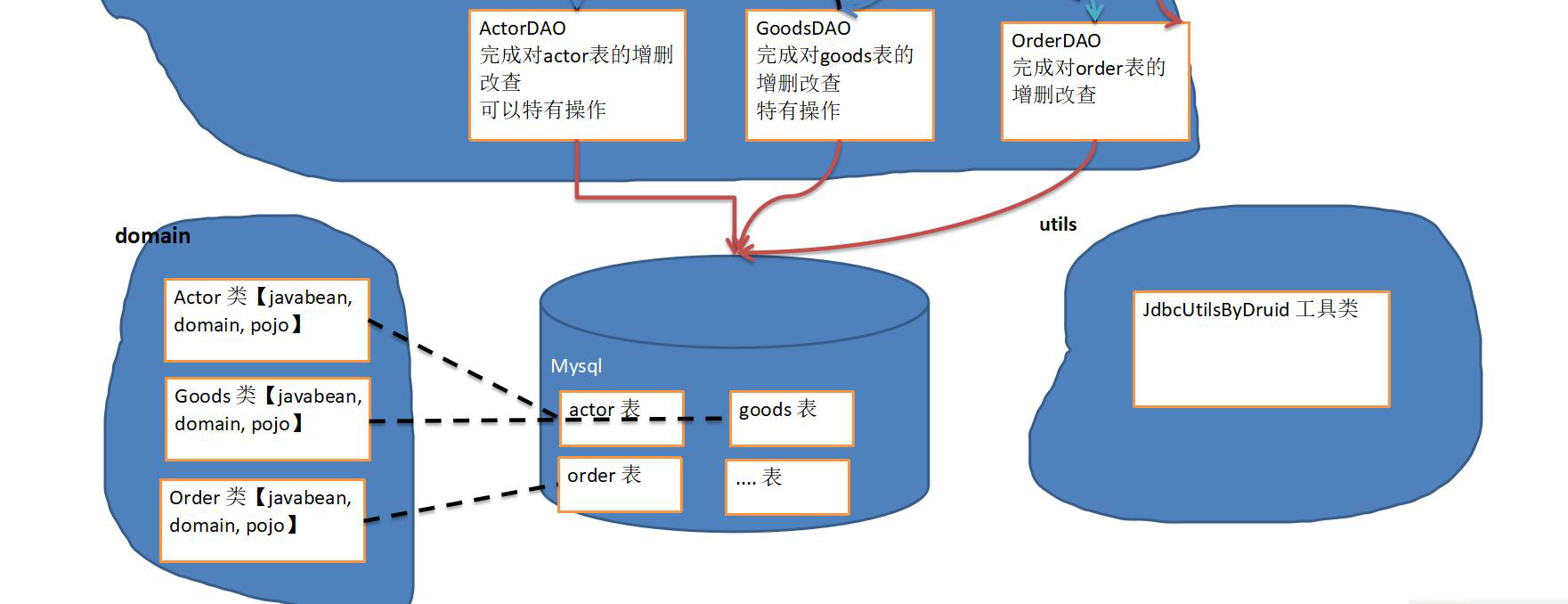
- BasicDao:可以设计成类、也可以设计成接口
14.10.2 domain/JavaBean/pojo 层:数据库对应的 java 类
14.10.3 service 层:具体业务层
14.10.3 view 层:页面层
14.11 封装 JDBC 工具类及使用
14.11.1 封装数据库连接功能
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
| public class JDBCUtils {
private static String user;
private static String password;
private static String url;
private static String driver;
static {
try {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream("src\\mysql.properties"));
user = properties.getProperty("user");
password = properties.getProperty("password");
url = properties.getProperty("url");
driver = properties.getProperty("driver");
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public static Connection getConnection() {
try {
return DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public static void close(ResultSet set, Statement statement, Connection connection) {
try {
if (set != null) {
set.close();
}
if (statement != null) {
statement.close();
}
if (connection != null) {
connection.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
| user=root
password=dimitre123
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:13306/hsp_db02
driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
|
14.11.2 使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
| import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.sql.*;
public class JDBCUtils_Use {
@Test
public void testSelect() {
Connection connection = null;
String sql = "select * from actor where id = ?";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet set = null;
try {
connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setInt(1, 5);
set = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
while (set.next()) {
int id = set.getInt("id");
String name = set.getString("name");
String sex = set.getString("sex");
Date borndate = set.getDate("borndate");
String phone = set.getString("phone");
System.out.println(id + "\t" + name + "\t" + sex + "\t" + borndate + "\t" + phone);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtils.close(set, preparedStatement, connection);
}
}
@Test
public void testDML() {
Connection connection = null;
String sql = "update actor set name = ? where id = ?";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setString(1, "周星驰");
preparedStatement.setInt(2, 4);
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtils.close(null, preparedStatement, connection);
}
}
}
|
14.11.3 封装成 Druid 工具类——将连接功能使用线程池实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| public class JDBCUtilsByDruid {
private static DataSource ds;
static {
Properties properties = new Properties();
try {
properties.load(new FileInputStream("src\\druid.properties"));
ds = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return ds.getConnection();
}
public static void close(ResultSet resultSet, Statement statement, Connection connection) {
try {
if (resultSet != null) {
resultSet.close();
}
if (statement != null) {
statement.close();
}
if (connection != null) {
connection.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/girls?rewriteBatchedStatements=true
username=root
password=root
initialSize=10
minIdle=5
maxActive=20
maxWait=5000
|
14.11.4 使用 Druid 工具类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| public class JDBCUtilsByDruid_USE {
public void testSelect() {
System.out.println("使用 druid方式完成");
Connection connection = null;
String sql = "select * from actor where id >= ?";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet set = null;
try {
connection = JDBCUtilsByDruid.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection.getClass());
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setInt(1, 1);
set = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
while (set.next()) {
int id = set.getInt("id");
String name = set.getString("name");
String sex = set.getString("sex");
Date borndate = set.getDate("borndate");
String phone = set.getString("phone");
System.out.println(id + "\t" + name + "\t" + sex + "\t" + borndate + "\t" + phone);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtilsByDruid.close(set, preparedStatement, connection);
}
}
}
|
- JDBCUtilsByDruid 的 connection 类型是 DruidPooledConnection,当 connection 关闭时,只是将连接的引用断开,连接还是在连接池内。
- JDBCUtils 的 connection 类型是 JDBC4connection,当 connection 关闭时,就真正实现了连接的关闭。
14.11.5 封装 DBUtils——实现关闭连接也能使用数据
第 15 章 正则表达式
常用正则表达式.txt
15.1 基本介绍
- 用某种模式去匹配字符串的一个公式。
15.2 快速入门
15.3 底层实现
15.4 语法规则
15.4.1 元字符
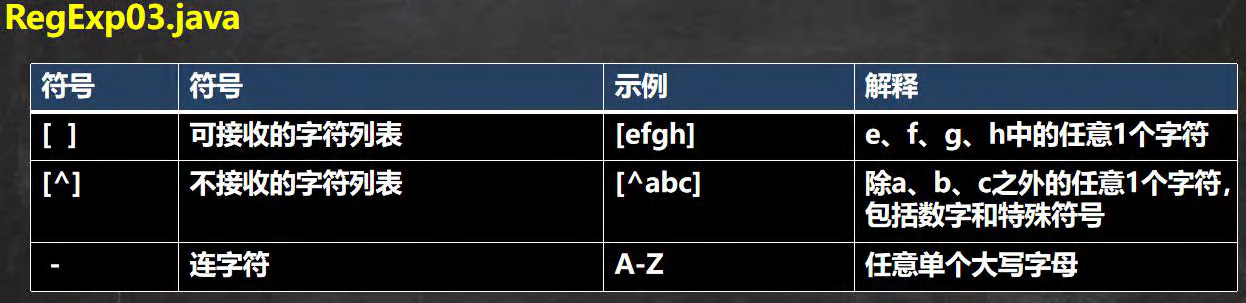
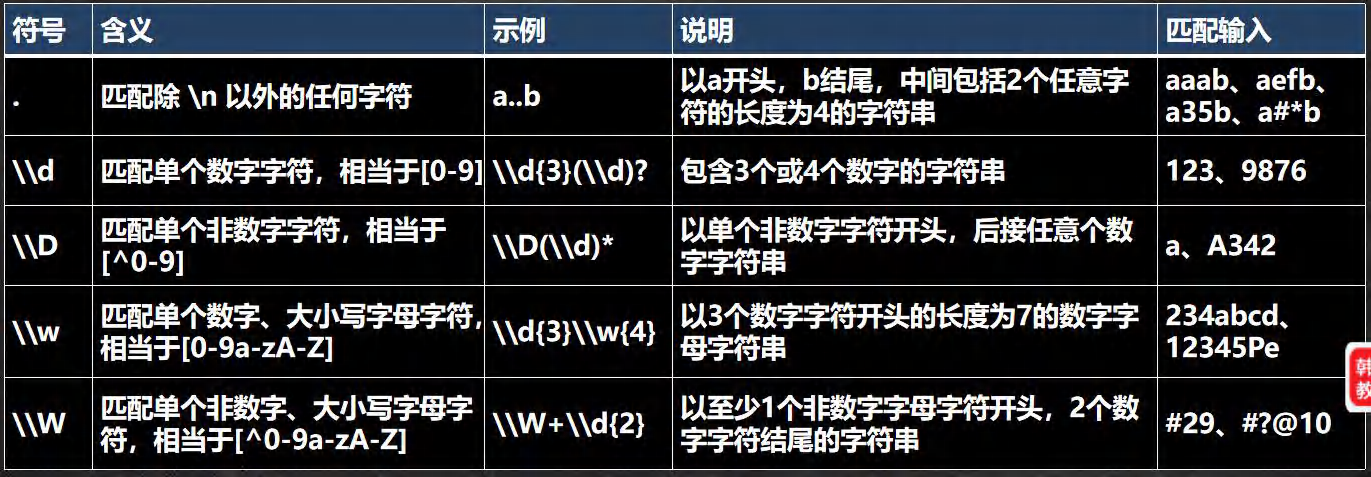
- 转义号
\\(注意是两个\代表一个\):需要转义的符号:.*+()/\?[]^{}
- 字符匹配符:
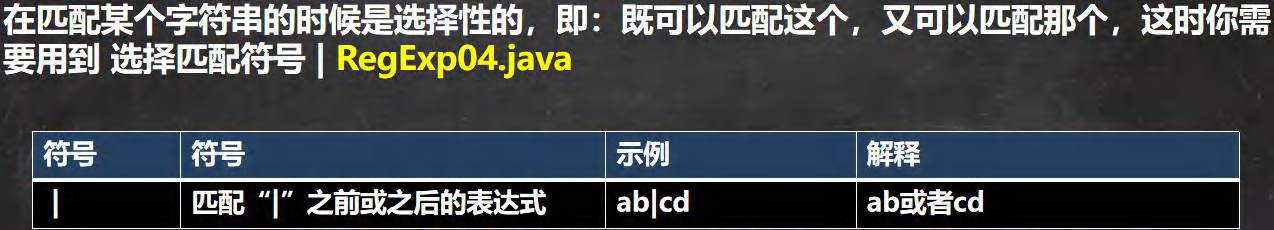
- 选择匹配符:
- 限定符:
- 用于指定其前面的字符和组合项连续出现多少次
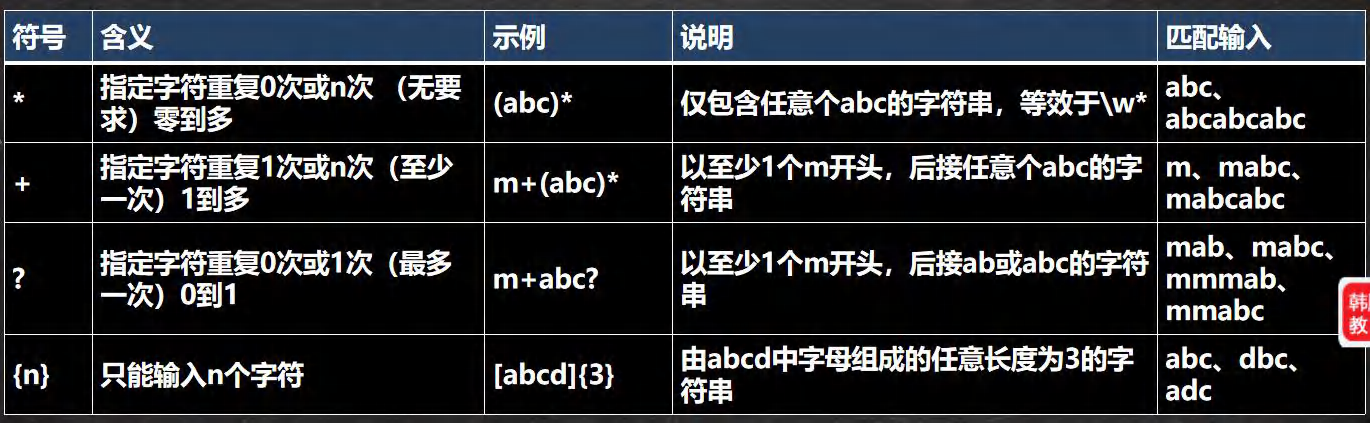
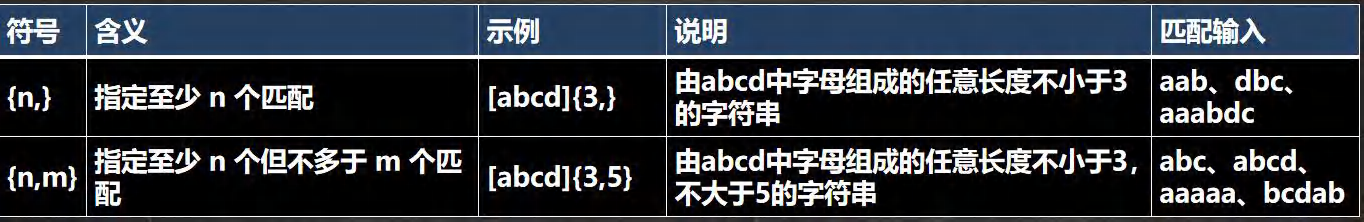
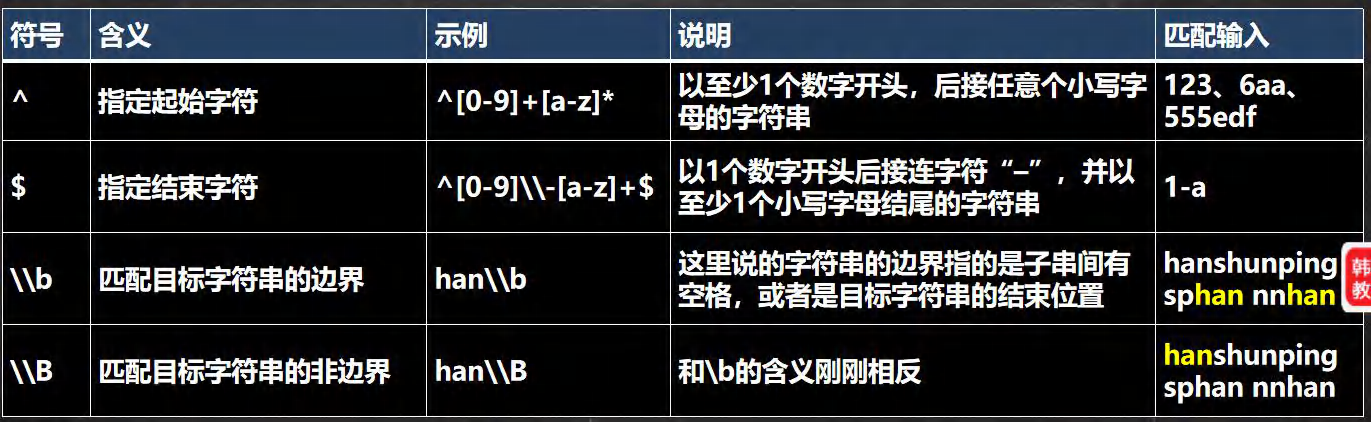
- 定位符:
- 规定要匹配的字符串出现的位置, 比如在字符串的开始还是在结束的位置
- 分组:
15.5 常用类

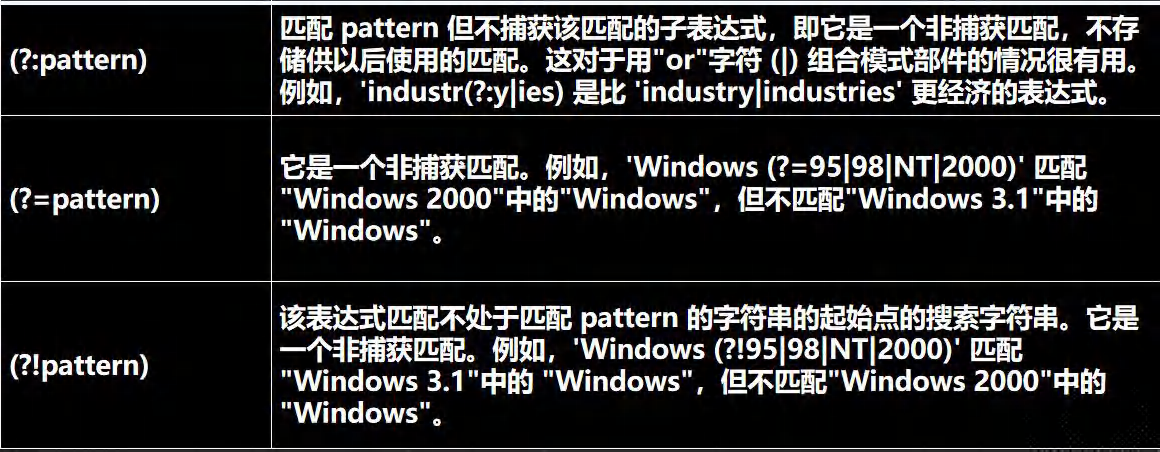
15.6 分组、捕获和反向引用

15.7 String 类中的正则
15.7.1 替换
public String replaceAll(String regex,String replacement)
15.7.2 判断
public boolean matches(String regex){} //使用 Pattern 和 Matcher 类
15.7.3 分割
public String[] split(String regex)
原文链接: https://sk370.github.io/2022/06/25/javase/Java语言基础(下)/
版权声明: 转载请注明出处。